Share this
Understanding Product Lifecycle Management
by Surefront on Feb 6, 2024 3:10:44 PM
Home > Blog > Understanding Product Lifecycle Management
Table of Contents
- The Definition of Product Lifecycle Management
- The Stages of Product Lifecycle Management
- The Benefits of Implementing Product Lifecycle Management
- Best Practices for Effective Product Lifecycle Management
- The Future of Product Lifecycle Management
Discover the importance of Product Lifecycle Management and how it can benefit your business.
The Definition of Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) refers to the process of managing a product throughout its entire lifecycle, from conception to disposal. It involves the coordination and integration of various departments and functions within a company, including design, engineering, manufacturing, marketing, and customer service. PLM aims to streamline and optimize the product development and management processes, ensuring that the right product is delivered to the right market at the right time.
In simpler terms, PLM is a strategic approach that helps companies effectively manage their products from birth to retirement. It encompasses activities such as product design, development, testing, production, marketing, sales, and support. By implementing PLM, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, increase product quality, and enhance customer satisfaction.
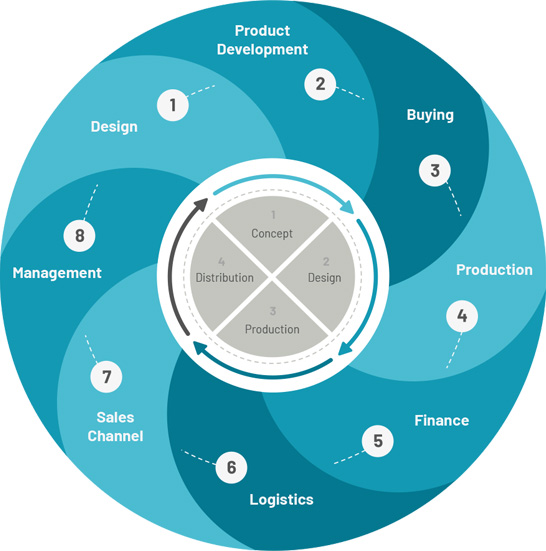
The Stages of Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management consists of several distinct stages. These stages are as follows:
1. Introduction: This is the initial stage where the product is introduced to the market. Companies focus on creating awareness and generating demand for the product.
2. Growth: In this stage, the product gains traction in the market and experiences a rapid increase in sales. Companies invest in marketing and sales efforts to capitalize on the growing demand.
3. Maturity: The product reaches its peak level of sales during the maturity stage. Competition intensifies, and companies may need to adjust their pricing, distribution, and promotional strategies to maintain market share.
4. Decline: As new products enter the market and consumer preferences change, the demand for the product declines. Companies may choose to discontinue the product or explore strategies to extend its life cycle.
Each stage of the product lifecycle requires careful management and decision-making to ensure the product's success and profitability.
The Benefits of Implementing Product Lifecycle Management
Implementing Product Lifecycle Management offers several benefits for businesses. These include:
1. Improved efficiency: PLM streamlines product development processes, reduces time-to-market, and enhances collaboration among cross-functional teams. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
2. Cost savings: By optimizing product design, manufacturing, and supply chain processes, PLM helps identify cost-saving opportunities. It minimizes rework, reduces material waste, and improves resource utilization.
3. Enhanced product quality: PLM ensures that products meet or exceed customer expectations by facilitating rigorous testing, quality control, and continuous improvement. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Increased innovation: PLM encourages innovation by providing a centralized platform for idea generation, design collaboration, and knowledge sharing. It fosters creativity and enables companies to bring new and innovative products to market.
5. Better decision-making: PLM provides real-time visibility into product data, performance metrics, and market trends. This enables informed decision-making and helps companies align their product strategies with market demands.
Overall, implementing PLM can give businesses a competitive edge by enabling them to develop and manage products more efficiently, effectively, and profitably.
Best Practices for Effective Product Lifecycle Management
To ensure effective Product Lifecycle Management, companies should consider the following best practices:
1. Cross-functional collaboration: Foster collaboration and communication among different departments involved in the product lifecycle, including design, engineering, manufacturing, marketing, and sales. This ensures alignment and reduces silos.
2. Robust data management: Implement a centralized PLM system that allows for efficient data storage, retrieval, and sharing. This ensures data integrity, version control, and accessibility across the organization.
3. Continuous improvement: Regularly evaluate and optimize product development processes to enhance efficiency, quality, and innovation. Embrace feedback from customers, stakeholders, and employees to drive continuous improvement.
4. Agile and flexible approach: Embrace agile methodologies and flexible product development approaches to adapt to changing market demands and customer feedback. This allows for quicker iterations and faster time-to-market.
5. Customer-centric focus: Keep the customer at the center of product development decisions. Understand their needs, preferences, and pain points to deliver products that provide value and meet their expectations.
By following these best practices, companies can maximize the benefits of PLM and achieve successful product lifecycle management.
The Future of Product Lifecycle Management
The field of Product Lifecycle Management is constantly evolving with advancements in technology and changing market dynamics. Some key trends shaping the future of PLM include:
1. Digitalization: PLM systems are becoming more integrated and intelligent, leveraging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. This enables better data-driven decision-making and automation of manual processes.
2. Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices allows for real-time monitoring and data collection throughout the product lifecycle. This data can be leveraged to optimize product performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve customer experiences.
3. Sustainability: With increasing awareness of environmental and social impacts, PLM is evolving to incorporate sustainability considerations. Companies are focusing on eco-friendly product design, responsible sourcing, and end-of-life product management.
4. Virtual and augmented reality: These technologies are being integrated into PLM systems to enable virtual prototyping, immersive design reviews, and enhanced collaboration among geographically dispersed teams.
5. Cloud-based PLM: Cloud-based PLM solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. They enable real-time collaboration, remote access to product data, and seamless integration with other enterprise systems.
As technology continues to advance, the future of PLM holds immense potential for driving innovation, improving efficiency, and delivering superior products to the market.
Share this
- PLM Software (36)
- PIM Software (29)
- Apparel & Fashion (20)
- Trending Topics (20)
- Merchandising (16)
- CRM Software (13)
- PLM Implementation (11)
- Catalog Management (6)
- Tech Packs (6)
- PLM RFP (5)
- Success Stories (5)
- Sustainability (5)
- Data Import (4)
- Line Sheet (4)
- Luxury Goods & Jewelry (4)
- Product Development (4)
- Retail (4)
- Supply Chain (4)
- Category Management (3)
- Home Furnishings (3)
- Wholesale (3)
- Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) (2)
- Cosmetics (2)
- Data Export (2)
- Health & Beauty (2)
- RFQ & Quote Management (2)
- Consumer Electronics (1)
- Import & Export (1)
- Industry Events (1)
- Inventory Management (1)
- Pet Stores (1)
- Purchase Orders (1)
- Report Builder (1)
- Textiles & Raw Materials (1)
- Unified Solution (1)
- Vendor Management (1)
- Visual First (1)
- White Paper or Case Study (1)
- workflow (1)
- October 2025 (3)
- September 2025 (3)
- August 2025 (4)
- April 2025 (4)
- March 2025 (3)
- January 2025 (8)
- December 2024 (5)
- November 2024 (3)
- October 2024 (5)
- September 2024 (6)
- August 2024 (2)
- July 2024 (1)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (4)
- April 2024 (5)
- March 2024 (3)
- February 2024 (2)
- December 2023 (4)
- September 2023 (2)
- August 2023 (5)
- July 2023 (3)
- June 2023 (2)
- May 2023 (2)
- April 2023 (4)
- March 2023 (5)
- February 2023 (3)
- January 2023 (5)
- December 2022 (4)
- November 2022 (3)
- October 2022 (4)
- September 2022 (5)
- August 2022 (4)
- July 2022 (2)
- May 2022 (1)
- February 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (1)
- September 2021 (1)
- May 2021 (1)
- April 2021 (1)
- February 2021 (1)
- May 2020 (1)